University of Antwerp
Services
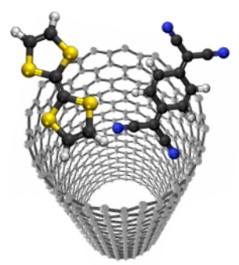
The core research task of UAntwerp within 3D Bricks will be to develop p- and n-type doped semiconducting carbon nanotubes (CNTs) through endohedral functionalisation, i.e. filling of CNTs (Figure 1). As such, the doping is expected to be highly stable, and in addition the outer surface of the CNTs remains free for complexation with DNA-origami to create 3D stacked transistors.
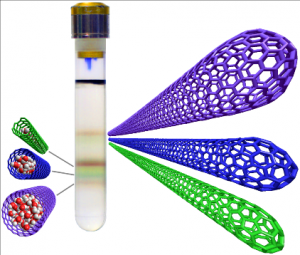
After filling, SWCNTs will also be sorted, either by density gradient ultracentrifugation (DGU) or by aqueous two-phase separation (ATPE) to obtain semiconducting SWCNTs with a defined chiral structure. While UAntwerp will focus on DGU, samples will be exchanged with KIT for ATPE sorting. An example of a DGU separation of empty and water-filled SWCNTs is presented in the adjacent Figure
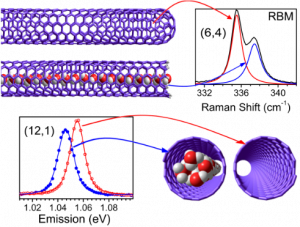
UAntwerp’s task is also to characterize the filling and the resulting doping with a series of experimental spectroscopic techniques, including optical absorption spectroscopy, NIR fluorescence-excitation spectroscopy, multiwavelength resonant Raman spectroscopy, hyperspectral PL imaging and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. In particular optical spectroscopy can be used for detecting the filling of SWCNTs as the vibrational and electronic signatures of the SWCNTs are known to shift upon filling with various molecules (expertise built up by the UAntwerp team).